I. Purpose of Data Mining Repositories
Data Mining Repositories store data for:
- Reporting
- Analysis
- Deriving insights
II. Data Warehouses
1. Definition
- A central repository of data integrated from multiple sources
- Act as a single “source of truth”, store historical and current data which has been cleansed, conformed and categorized.
- When data gets loaded into data warehouse, it is ready modeled and structured for purposes.
- Can store:
- Relational data: CRM, ERP, HR and Finance applications
- Non-relational data
2. Architecture
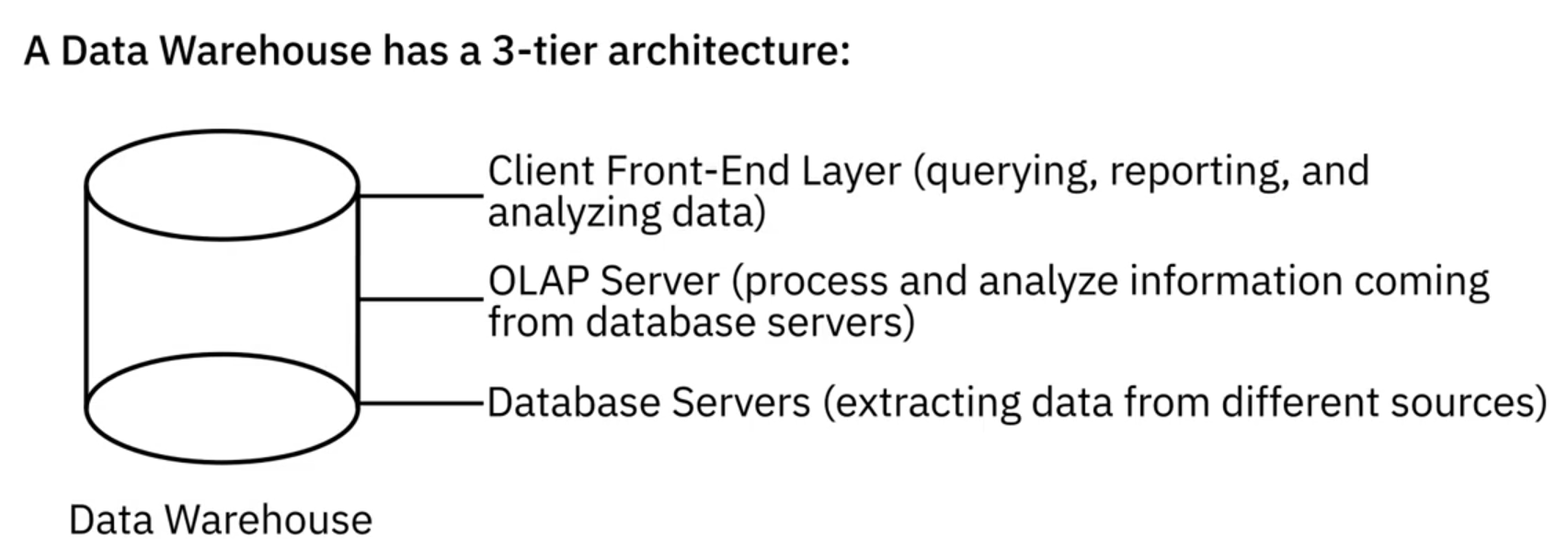
3. Cloud-based data warehouses
Nowadays, data warehouses are moved into clouds. Benefits
- Lower costs
- Limitless storage and compute capabilities
- Pay as you go
- Faster recovery
4. Usage
=> Use data warehouse when have massive of data and need to be rapidly available for reporting and other purposes.
Popular Providers
- teradata
- Oracle Exadata
- IBM Db2
- Netezza
- AWS Redshift
- Google BigQuery
- Cloudera
- Snowflake
III. Data Marts
1. Definition
- Data Marts are sub-section of Data Warehouses, that are built for specifically for particular business function, purpose, or community of users.
Examples: - Data Scientists access customers’ session data in a specifically built data mart to build a recommender.
2. Types of Data Marts
There are 3 types of Data Marts:
- Dependent Data Marts
- Independent Data Marts
- Hybrid Data Marts
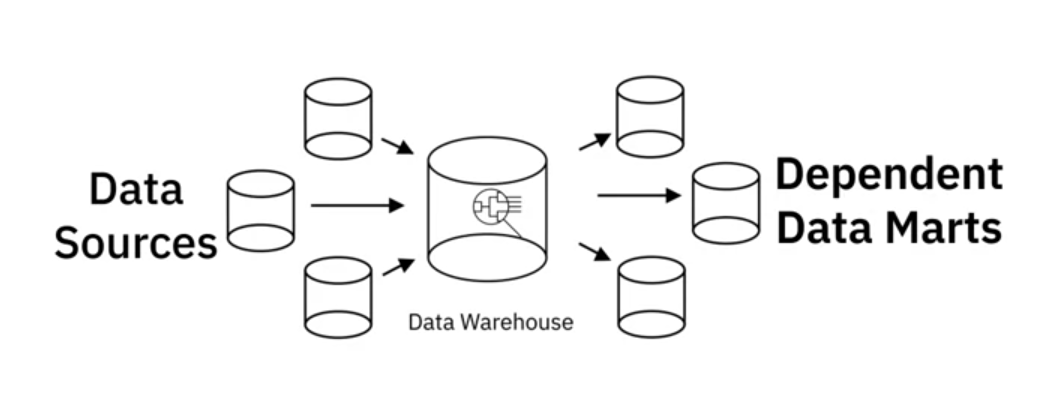
a) Dependent Data Marts
- Sub-section of an Enterprise Data Warehouse
- Data source has been cleansed and transformed
- Offers analytical capabilities of a restricted area of a data warehouse => provides isolated performance and isolated security.
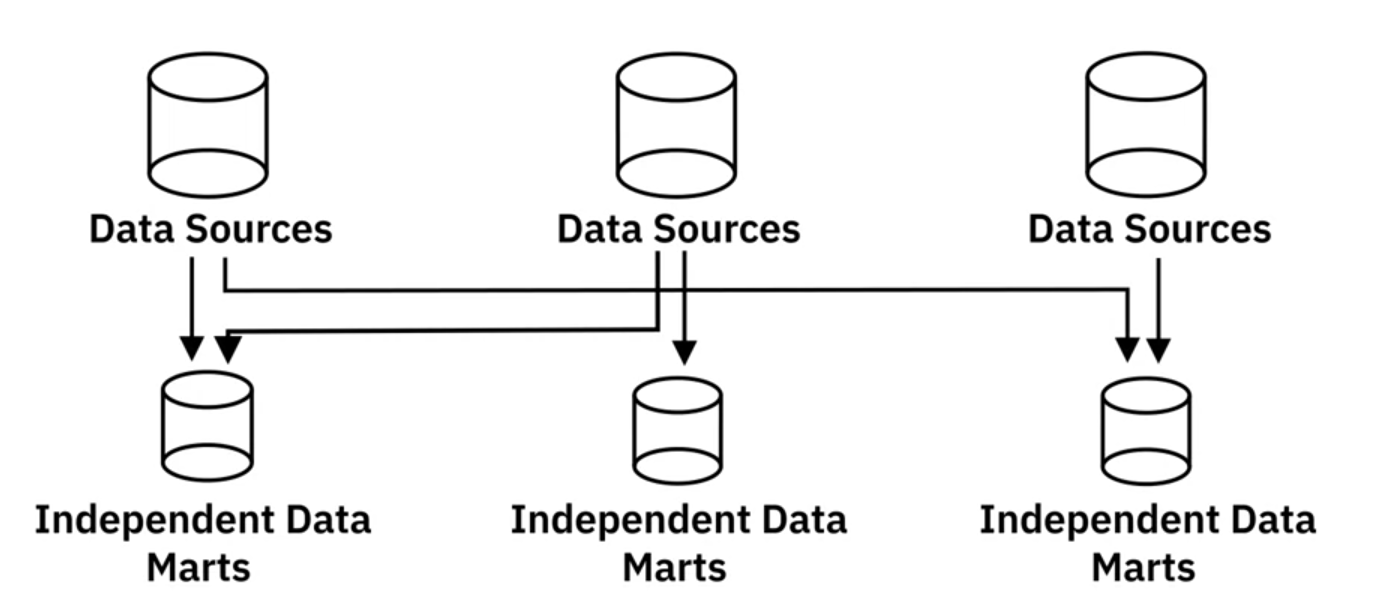
b) Independent Data Marts
- Created from other sources than Enterprise Data Warehouses, such as Internal Operational Systems or External Data.
- Must clean and transform the data itself, since data is from the source directly.
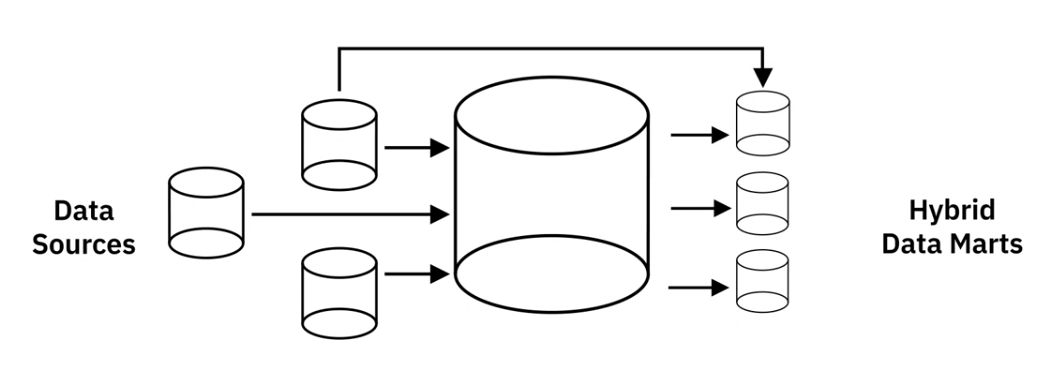
c) Hybrid Data Marts
- Combination of Dependent and Independent Data Marts, which means the data sources are from Data Warehouse and others (Internal Operational Systems or External Data)
3. Purpose of Data Marts
- Provide data to users when they need it.
- Accelerate business processes.
- Provide cost and time efficient way to make data-driven decision
- Improve user response time
- Provide security and control
IV. Data Lakes
1. Definition
- Is a data repository that store semi-structured and unstructured in their native (raw) formats.
- While Data Warehouse’s data has been cleansed and transformed, data in data lakes can be loaded without defining the structured and schema of data.
- Data is appropriately classified, protected and governed.
- Can be deployed using:
- Cloud Object Storage, such as Amazon S3.
- Large-scale distributed systems such as Apache Hadoop
- RDBMS, NoSQL
2. Benefits
- Store all types of data
- Scale based on storage capacity
- Saving time in defining structures, schemas, transformations (data is imported in its raw format)
- Serving in different use cases and ways